In 2004, scientists at the University of Manchester first isolated and investigated graphene, the supermaterial composed of single-layer carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice.
Since then, it has become a wonder, with properties that make it extremely useful in numerous applications. Among scientists, it is generally believed that about 1.9% of carbon in the interstellar medium (ISM) exists in the form of graphene, with its shape and structure determined by the process of its formation.
As it happens, there could be lots of this supermaterial on the surface of the Moon. In a recent study, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Science (CAS) revealed naturally formed graphene arranged in a special thin-layered structure on the Moon.
These findings could have drastic implications for our understanding of how the Moon formed and lead to new methods for the manufacture of graphene, with applications ranging from electronics, power storage, construction, and supermaterials.
They could also prove useful for future missions that will create permanent infrastructure on the lunar surface.
The team was led by professors Wei Zhang and Meng Zou from the Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering and the Jilin Provincial International Cooperation Key Laboratory of High-Efficiency Clean Energy Materials at Jilin University, Jilin University senior engineer Xiujuan Li, and Wencai Ren from the CAS' Institute of Metal Research (CAS-ISM).
They were joined by colleagues from multiple Key Laboratories at Jilin University, the CAS-ISM, the Deep Space Exploration Lab, and the Lunar Exploration and Space Engineering Center. The paper that describes their findings appeared in the National Science Review.
For decades, scientists have speculated that the Earth-Moon system was formed from a massive collision – the Giant Impact Hypothesis – between a Mars-sized body (Theia) and Earth roughly 4.4 billion years ago.
This theory is supported by analyses of the moon rocks returned by the Apollo astronauts, which led to the notion of a carbon-depleted. However, recent findings have come to challenge this consensus based on the observation of global carbon ion fluxes on the Moon, which suggest the presence of indigenous carbon.
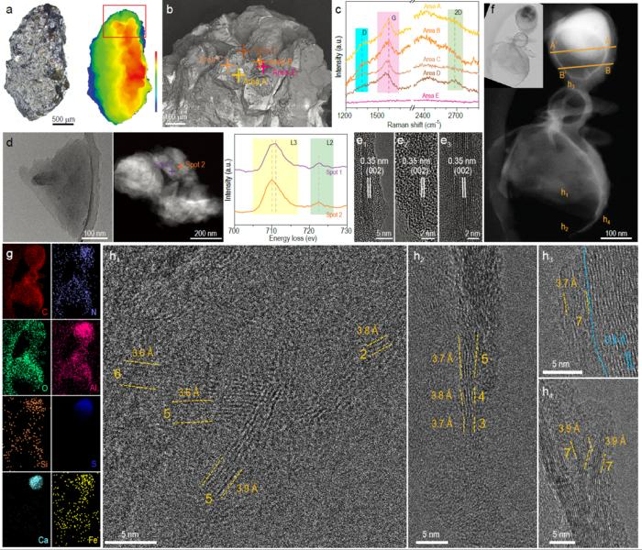
These observations are consistent with the analysis of one of the Apollo 17 samples that showed the presence of graphite. For their study, the team conducted a spectroscopic analysis of an olive-shaped sample of lunar soil (measuring about 2.9 mm by 1.6 mm) retrieved by the Chang'e 5 mission in 2020.
This was China's third robotic mission to reach the lunar surface and its first sample return from the Moon. From the spectra they obtained, they found an iron compound in a carbon-rich section of the sample that is closely related to the formation of graphene.
Upon further analysis using advanced microscopic and mapping technologies, they confirmed that the carbon in the sample was graphene flakes two to seven layers thick.
In terms of how it got there, the team proposed that the graphene may have formed during a period of volcanic activity early in the Moon's history when it was still geologically active.
They further hypothesize that the graphene was catalyzed by solar winds that kicked up the lunar regolith and its iron-containing minerals, which could have helped transform the carbon's atomic structure.
They also allow for the possibility of meteorite impacts, which are also known to create high-temperature and high-pressure environments similar to volcanic activity. As they state in their paper:
"Graphene is embedded as individual flakes or formed as part of a carbon shell enclosing the mineral particles. Our result reveals one typical structure of indigenous carbon in the Moon and its formation mechanism has been proposed. This finding may reinvent the understanding of chemical components, geography episodes and the history of the Moon."
These findings could also have a tremendous impact on research here on Earth, where graphene is being investigated for applications ranging from electronics and mechanics to materials science.
As they indicate in their study, this study could lead to new methods for inexpensively producing the material and offer additional opportunities for lunar exploration:
"The identification of graphene in the core–shell structure suggests a bottom-up synthesis process rather than exfoliation, which generally involves a high-temperature catalytic reaction. Therefore, a formation mechanism of few-layer graphene and graphitic carbon is proposed here…
"In turn, the mineral-catalysed formation of natural graphene sheds light on the development of low-cost scalable synthesis techniques for high-quality graphene. Therefore, a new lunar exploration program may be promoted and some forthcoming breakthroughs can be expected."
These findings could also prove useful for future missions that will lead to the development of permanent infrastructure on the lunar surface. This includes NASA's Artemis Program, which aims to create a "sustained program of lunar exploration and development."
There's also the ESA's Moon Village initiative and China and Russia's plan for an International Lunar Research Station (ILRS). In addition to exploration and scientific research, these programs could conduct experiments on the properties and uses of graphene, which could include the manufacture of lunar habitats!
This article was originally published by Universe Today. Read the original article.
